“Everyone takes it, so should I?” The Truth About Red Ginseng
If you have an interest in Asian wellness trends or have visited a Korean household, you’ve likely encountered Red Ginseng. It is the undisputed king of health supplements in South Korea—the go-to gift for holidays and the first thing people reach for when they feel burned out. I, too, find myself instinctively tearing open a ginseng stick when work deadlines pile up. There is something about that bitter, earthy taste that seems to trigger a placebo effect of instant energy.
But here is the important question: Do we actually know what we are consuming?
Many people take it simply because “it’s supposed to be good for you,” without considering their body constitution or current medications. Surprisingly, this blind approach can lead to issues like heartburn, headaches, or simply wasting money on a product your body can’t absorb.
Today, as a health curator who has analyzed countless guidelines and studies, I’m going to break down the real benefits of Red Ginseng and how to choose a product that actually works. If you want to know if that ginseng shot is medicine or just expensive sugar water for you, keep reading.

Why is Red Ginseng Considered a “Superfood”?
Red Ginseng is essentially fresh ginseng that has been steamed and dried. This process is crucial because it causes a chemical change in the root. During steaming, the types and amounts of Saponins—specifically called ‘Ginsenosides’—are optimized.
The Key is “Ginsenosides” When health authorities evaluate the quality of Red Ginseng, they look at specific markers: the sum of Ginsenosides Rg1, Rb1, and Rg3.
If you look at the nutrition label on the back of a box, these numbers act as the product’s “spec sheet.”
Editor’s Note: Don’t be fooled by marketing claims like “100% Red Ginseng Extract.” If that extract is heavily diluted with water, the percentage might be 100%, but the actual active ingredients could be negligible. Always check the specific milligram count of Ginsenosides.
5 Scientifically Recognized Benefits
Based on guidelines from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) and various studies, Red Ginseng is recognized for five primary health benefits. These aren’t just folk remedies; they are backed by human application tests.
1. Boosting the Immune System This is the most famous benefit. Ginseng helps your body’s defense system fight off external viruses and bacteria. Studies suggest that ginseng extracts stimulate macrophage activity, which helps regulate immune responses.
2. Fighting Fatigue It’s not just for physical exhaustion; it also helps with mental fatigue caused by stress. It is deeply involved in the body’s energy production process and helps suppress the accumulation of lactic acid (the substance that makes you feel tired).

3. Improving Blood Circulation Ginseng helps inhibit platelet aggregation, meaning it stops your blood from becoming too “sticky” and clotting unnecessarily. Improved blood flow means oxygen and nutrients are delivered more efficiently throughout the body. This is a major reason why middle-aged adults prioritize ginseng for cardiovascular health.
4. Memory Improvement and Antioxidant Effects Worried about brain fog? Red Ginseng can positively influence neurotransmitters, potentially aiding memory retention. Additionally, it has antioxidant properties that help eliminate free radicals in the body, which are responsible for aging and cellular damage.
5. Menopausal Health (Specific Dosage Required) Recently, certain ginseng products have been recognized for helping with menopausal symptoms in women. However, this benefit is usually tied to a specific, higher concentration of Ginsenosides (often 25mg or more), so check the label carefully if this is your goal.
“I Feel No Difference.” Is Absorption the Problem?
This is the most critical part of this guide. Have you ever thought, “I bought the expensive brand, but I don’t feel any different?”
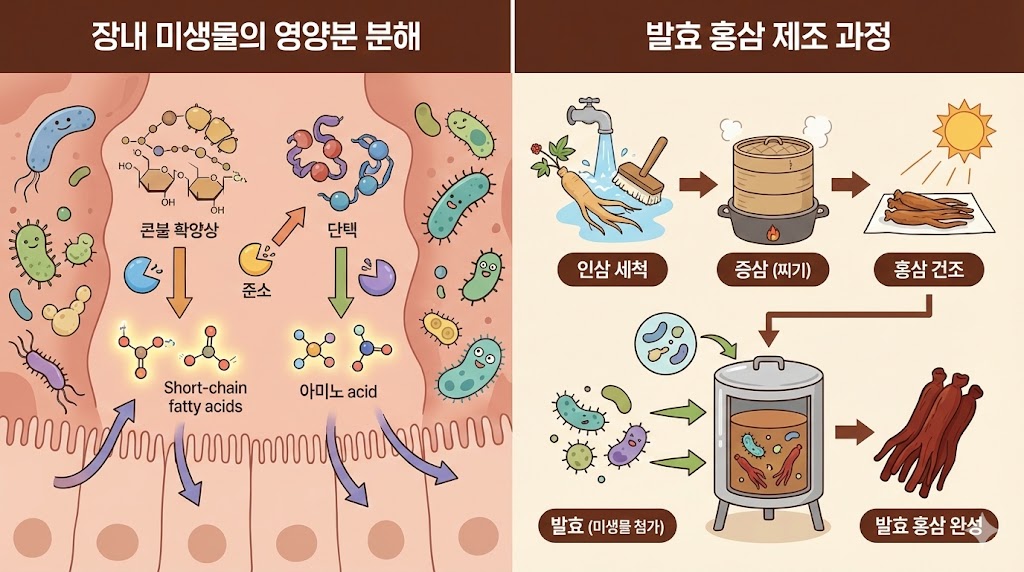
It might not be the product’s fault; it might be your gut microbiome.
1 in 4 People Cannot Absorb Ginseng The Ginsenosides in ginseng are large molecules. On their own, they are too big to be absorbed by the human body. They must be broken down into a smaller metabolite called ‘Compound K’ by specific gut bacteria (like Prevotella oris).
However, research suggests that about 25% of the population lacks the specific gut bacteria needed to break down ginseng. Even among the remaining 75%, the ability to break it down varies wildly. In other words, for some people, drinking expensive ginseng is literally flushing money down the toilet.
The Solution: Fermented Ginseng? To bypass this issue, the industry has developed ‘Fermented Red Ginseng’ (enzyme-treated). This process mimics human digestion, breaking the Ginsenosides down into Compound K before you even drink it. If you haven’t felt the effects of standard ginseng, trying a fermented product or one containing “Compound K” might be the game-changer you need.

Important Safety Precautions
Even natural supplements can have side effects. If you have underlying conditions or take medication, proceed with caution.
- Diabetes and Blood Thinners: Red Ginseng lowers blood sugar and inhibits blood clotting. If taken with diabetes medication or anticoagulants (like Warfarin), it can amplify the drug’s effects, potentially leading to hypoglycemia or bleeding risks. Consult your doctor first.
- Upcoming Surgery: Due to its blood-thinning properties, it is generally recommended to stop consumption at least one week before any major surgery.
- “Heat” Constitution (Sensitivity): In traditional medicine, ginseng is considered “warming.” If you naturally have a lot of body heat, get flushed easily, or sweat profusely, high doses might cause headaches, facial flushing, or insomnia. Start with a small dose to see how you react.
- Caffeine Interaction: Taking ginseng with coffee or energy drinks can overstimulate the nervous system, leading to jitters or insomnia. It is best to leave a time gap between them.
3 Criteria for Choosing the Best Product
Ignore the brand name for a moment and look at the facts. Here is how to pick a winner:
- Look for the ‘Health Functional Food’ Mark: Products labeled merely as “Ginseng Drink” or “Tea” often contain very little actual ginseng. Look for the official certification mark from your local food safety authority (like the MFDS mark in Korea) to ensure it meets functional standards.
- Check Ginsenoside Content (Rg1+Rb1+Rg3): To expect real health benefits, the sum of these three components should be at least 3mg per daily serving. (Note: Specific goals like menopausal support may require higher doses).
- Watch Out for Additives and Sugar: Ginseng is naturally bitter. To mask this, many manufacturers load their sticks with high-fructose corn syrup or sugar. Check the ingredient list to ensure you aren’t just buying an expensive sugar rush.
Conclusion: Consistency is Key
Red Ginseng is not a magic potion. You won’t turn into Superman overnight. However, if you choose a high-quality product that fits your body type and consume it consistently for at least 3 months, it can be a powerful ally in reclaiming your vitality.
Tonight, why not take a moment to check the ingredient label of the ginseng sitting in your pantry? It might be time for an upgrade.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Should I take it on an empty stomach or after a meal? A. generally, absorption is known to be better on an empty stomach. However, ginseng can be potent. If you have a sensitive stomach or experience heartburn, it is better to take it 30 minutes to an hour after a meal.
Q2. Can children take adult ginseng? A. It is not recommended. Children’s metabolism and body weight are different. Giving them adult dosages can lead to side effects like hyperactivity or digestive issues. Please stick to products specifically formulated for children with adjusted dosages.
Q3. Is it safe to eat expired ginseng? A. Liquid products should be discarded immediately as they can spoil. While dried roots might be safe if stored perfectly, it is risky. For your safety, do not consume expired products.
Q4. Will taking ginseng in the summer make me too hot? A. This is a common myth. There is no medical evidence that ginseng raises core body temperature. In fact, it can help restore energy lost through sweating in the heat. However, if you are personally sensitive to “warming” foods, use caution.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog post is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider regarding any medical condition or before starting any new supplement regimen.g can be a natural and reliable ally for long-term health.
